Australia now boasts over 1,000 Bitcoin ATMs, positioning it third in the world after the United States and Canada.
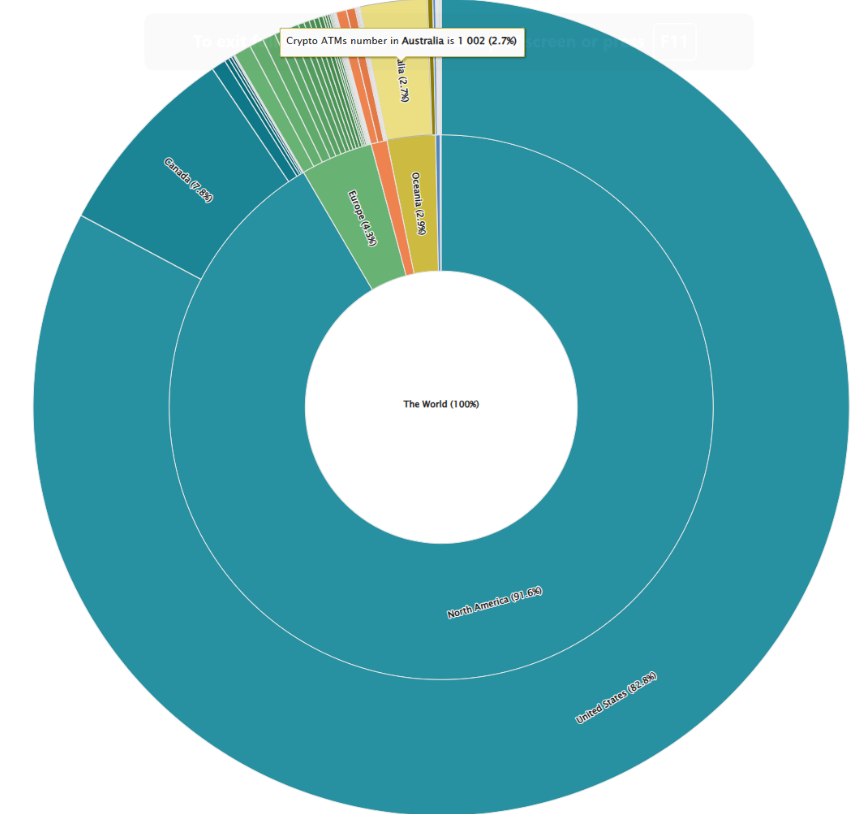
As of April 24, Australia has accumulated 1,002 operational Bitcoin ATMs, positioning it as the third nation to accomplish this milestone, following the United States and Canada. The country comprises 2.7% of the Bitcoin ATM network worldwide.
According to data from Coin ATM Radar, the United States had its first 1,000 cryptocurrency ATMs in November 2017, while Canada did so in January 2021.
The United States currently houses 82.8% of the worldwide Bitcoin ATM fleet, consisting of 31,170 machines, while Canada accounts for 7.8% of the total with 2,918 cryptocurrency ATMs.
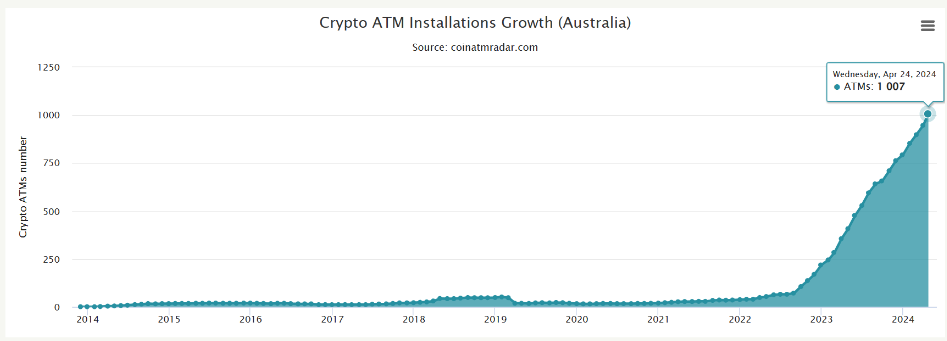
Australia was historically a dormant market for cryptocurrency ATMs. However, since the conclusion of 2022, adoption has escalated exponentially due to the involvement of private enterprises.
The number of Bitcoin ATMs in Australia exceeded that of Asia in April 2023. This region comprises significant economies, including China, Japan, Singapore, and India.
Australia is well-positioned to surpass Europe, which currently has 4.3% (1,617 machines) of all operational Bitcoin ATMs, at the present installation rate.
“Just last week, we had the fourth BTC halving and the market was panicking over the outbreak of war in the Middle East (which has since de-escalated).”
Additional nations that possess substantial numbers of cryptocurrency ATMs are El Salvador (215), Poland (211), Germany (194), and Hong Kong (157).
The revenue of a crypto ATM company is unaffected by fluctuations in the price of Bitcoin.
Recently, Cointelegraph reported that hackers who previously leaked the database of El Salvador’s Bitcoin ATMs have published a portion of the source code for the state-operated Chivo Bitcoin wallet.
The hacker group CiberInteligenciaSV wrote in a public forum, “This time, I bring you the code inside the Bitcoin Chivo Wallet ATMs in El Salvador. Remember that it is a government wallet, and as you know, we do not sell; we publish everything for free for you.”
On April 22, the local cybersecurity initiative VenariX issued a public alert via X regarding an imminent breach. It referenced the Telegram channel of CiberInteligenciaSV, which contained messages regarding the publication of the source code.



