The Beam Chain combines several expensive enhancements, such as quick finality and native zero-knowledge proof compatibility, into a single Ethereum upgrade.
The Ethereum community last came together for a major tech event over two years ago. The so-called Ethereum merge signaled the long-awaited transition of the network to a new, environmentally friendly consensus method known as “proof-of-stake.”
Since then, much has stayed the same in the Ethereum blockchain’s fundamental architecture. The Ethereum community has largely been deprived of a single organizational vision—at least one that commanded the degree of enthusiasm produced by the Merge—while the chain’s developers have pushed through several enhancements to facilitate the establishment of rapid and inexpensive “layer-2” blockchains.
That could change shortly.
At Tuesday’s Ethereum Devcon conference in Bangkok, researcher Justin Drake of the Ethereum Foundation presented his idea for a significant overhaul of the Ethereum consensus layer, dubbed “Beam Chain.”
“A proposed redesign of the consensus layer that incorporates all of the latest and greatest ideas from the Ethereum roadmap,” Drake described Beam Chain during a keynote at the Queen Sirikit National Convention Centre in Bangkok.
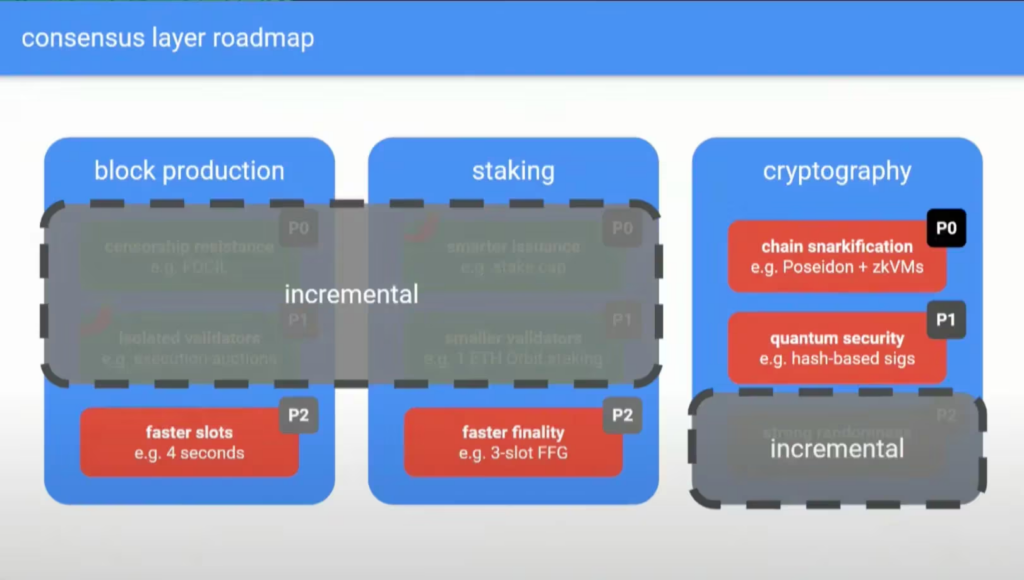
Several “big ticket” improvements to Ethereum’s consensus layer are bundled under Drake’s Beam Chain concept. The modifications affect how Ethereum manages staking and zero-knowledge cryptography and its block generation machinery.
Following months of rumors on the internet and in cryptocurrency forums that the prominent Ethereum researcher, who had a vital role in the 2022 Merge upgrade, was working on something significant, Drake’s talk was eagerly awaited. Drake spoke to a crowded convention center, with spectators swarming into the corridor behind the main stage.
Ethereum won’t undergo any immediate changes due to the Beam Chain, nor will it undergo any significant modifications from the current roadmap. However, it suggests a substantial alteration to the structure of Ethereum’s upcoming updates.
Ethereum now updates its basic code about once a year. Drake suggests that to solve the problem of “low-hanging fruit,” the chain should continue to undergo little improvements annually. However, after a few years, he plans to implement significant changes simultaneously.
The Beam Chain would concentrate on Ethereum’s consensus layer, also known as the Beacon Chain, which manages the processing and recording of transactions on the network. Drake remarked, “The beacon chain is kind of old.” “The spec was frozen five years ago, and in those five years, so much has happened.”
Drake claims that modern Ethereum developers have a “much better understanding” of adjusting to maximize extractable value—strategies experienced traders employ to extract additional profit from Ethereum, often at the expense of ordinary users. According to Drake, the Ethereum blockchain has accrued “technical debt” that hinders developers’ capacity to create the chain swiftly and securely, and the last five years have also seen significant advancements in zero-knowledge technology.
The Beam Chain will prioritize “faster slots” and “faster finality,” which entails raising the number of transactions in each block and scaling up the frequency at which blocks are added to the chain. This could result in the implementation of single-slot finality, which allows blocks containing transaction data to be finalized instantly, making the data irrevocable and unchangeable.
On Ethereum, it currently takes around 15 minutes for a block to complete. The finalization process would become more efficient for applications or exchanges with a high transaction flow by reducing the finality time. The 15-minute delay increases the probability of reorganizations and allows MEV to be removed.
However, as more processing power and costly gear are required, there are also worries regarding centralization with quicker finalization times. Developers must weigh the trade-off between processing power and reducing finalization times.
Additionally, the Beam Chain proposes to further integrate zero-knowledge cryptography into Ethereum’s base network’s fiber.
Ethereum developers have adopted a roadmap that includes layer-2 rollups, which are auxiliary blockchains built on top of Ethereum that allow for faster and less expensive transaction execution before being settled down to the base chain.
As part of it, rollups have adopted a novel technology that aids in blockchain scaling by utilizing zero-knowledge proofs. Numerous ZK rollups, such as Matter Labs’ zkSync and Polygon’s zkEVM, have emerged in the past two years, generating a lot of interest in and developing these new blockchains.
A zero-knowledge proof will be incorporated into the main Ethereum layer-1 chain using Drake’s Beam Chain proposal. Therefore, one would question what this might mean for the rapidly expanding field of ZK-powered layer-2 networks.
Drake stated in his talk on Tuesday that he was hesitant to refer to the ambitious Beam chain update as “Ethereum 3.0” (people occasionally referred to Ethereum’s 2022 Merge upgrade as “Ethereum 2.0.”) Drake stated, “The Beam Chain is only about the consensus chain,” adding that additional research is still being conducted on Ethereum’s data and execution layers, which are the other essential components of the network that handle layer-2 data and applications.



