Interoperable blockchains are redefining the future of Web3 by cutting down silos and enabling seamless data and asset exchange across networks.
Here we’ll delve into the significance of interoperable blockchains, major enabling technologies like IBC and cross-chain bridges, challenges like security and standardization, and how innovation is driving the evolution of a unified, scalable, and user-friendly decentralized ecosystem.
Understanding Interoperable Blockchains
Interoperable blockchains are the ability of different blockchain networks to connect, share data, and perform transactions across platforms without the use of intermediaries.
Simply put, blockchains can interact effortlessly and trustlessly, regardless of their protocols, consensus mechanisms, or native tokens.
As the crypto ecosystem grows, the need for building interoperable blockchains becomes clear. Currently, many blockchains operate as separate silos, making it difficult for users and developers to transfer assets or data between networks such as Ethereum, Solana, and Avalanche.
Interoperable blockchains address this fragmentation by enabling cross-chain communication and collaboration.
Types of Blockchain Interoperability
There are two major types of interoperable blockchains:
Vertical Interoperability
Vertical interoperability takes place inside the layers of a single blockchain network. It guarantees that different levels communicate seamlessly, such as Layer 1 (the base layer) and Layer 2 (scaling solutions like rollups).
For example, Ethereum and its Layer 2s, like Arbitrum and Optimism, show vertical interoperability via protocol alignment and shared security models.
Horizontal Interoperability
Horizontal interoperability refers to communication and interaction across different blockchain platforms. This includes sending tokens or executing smart contracts between chains such as Ethereum and Binance Smart Chain, or Cosmos and Polkadot.
Different consensus algorithms, token standards, and governance frameworks make achieving horizontal interoperability more complex.
Interoperability enables:
- Secure cross-chain communication with protocols like IBC (Inter-Blockchain Communication) and LayerZero.
- Cross-chain data sharing enables dApps to access real-time data across networks.
- Smart contract integration across ecosystems, allowing developers to create apps that run on multiple blockchains simultaneously.
In essence, interoperable blockchains establish the foundation for a unified crypto ecosystem where users have a frictionless experience, developers can build with composability, and value flows freely across chains.
Why Building Interoperable Blockchains Matters
As the blockchain environment continues to expand, the need for a unified crypto ecosystem becomes increasingly critical.
While individual blockchains such as Ethereum, Solana, and Binance Smart Chain offer useful features, their isolated nature poses significant challenges for users, developers, and businesses alike.
This siloed environment emphasizes the significance of developing interoperable blockchains.
The Problem With Blockchain Silos
Most blockchain networks already function as autonomous ecosystems. Each has its own consensus mechanism, smart contract standard, tokenomics, and governance framework. This incompatibility leads to siloed chains that cannot communicate with one another natively.
These isolated systems pose three key concerns:
Fragmented Liquidity and Capital Inefficiency
Tokens usually tie within a single blockchain, resulting in fragmented liquidity. Avalanche tokens, for example, cannot be utilized directly in an Ethereum-based DeFi application without complex bridging.
This fragmentation diminishes overall capital efficiency, increases slippage in DEX trades, and hinders users’ ability to capitalize on cross-chain opportunities.
Poor User Experience
Blockchain interoperability is critical to improving the user experience. In today’s fragmented crypto world, users must juggle multiple wallets, manage gas fees in different native tokens, and navigate disparate user interfaces.
This disjointed experience delays adoption and increases the risk of human mistakes.
Developmental Constraints and Innovation Bottlenecks
When blockchains do not interoperate, developers are forced to build within the confines of a single chain. This limits access to larger liquidity pools, oracles, and data feeds.
It also limits the composability, the ability to combine protocols like building blocks of decentralized apps (dApps), inhibiting innovation.
Advantages of Building Interoperable Blockchains
Overcoming these barriers through interoperability results in a more vibrant, efficient, and user-friendly crypto ecosystem. Here are the main benefits:
Improved Liquidity and DeFi Accessibility
Interoperable blockchains enable assets and liquidity to flow freely between networks. This allows users to deposit assets on one chain and use them on another, optimizing capital use and making DeFi protocols more accessible and efficient.
For example, interoperability protocols such as Thorchain and Cosmos’ IBC allow native assets to be swapped across chains without the use of wrapped tokens.
Enhanced Scalability and Specialization
Interoperability enables chains to focus on their strengths. For example, one chain may specialize in speed and throughput, whilst another focuses on security and finality.
Connecting these specialized networks improves the ecosystem’s scalability and robustness. Polkadot, for example, promotes this concept with “parachains,” each adapted for a specific use case yet connected through a central relay chain.
Accelerated Developer Innovation through Composability
When blockchains can interact natively, developers can access features from several ecosystems. A dApp could obtain identification verification from one chain, pricing data from another, and then execute on the third.
This type of modular development boosts productivity, reduces redundancy, and results in more powerful, feature-rich apps.
Greater Network Effects and Adoption
The more interoperable blockchains become, the more network effects are unlocked. Users benefit from increased utility, while developers gain access to a larger market.
This synergy has the potential to boost mass adoption by abstracting away the complexity associated with using multiple blockchains.
Ultimately, building interoperable blockchains is more than just a technical enhancement; it is a fundamental shift that brings the crypto industry closer to a truly decentralized, inclusive, and user-centric future.
Interoperability connects isolated ecosystems, allowing value, data, and logic to flow freely across a global digital economy.
Leading Projects and Protocols that Drive Interoperability
As the blockchain ecosystem grows, interoperability across diverse networks becomes increasingly important. Several initiatives and protocols have emerged to address this issue, each providing distinct solutions for seamless cross-chain communication and asset transfers.
Polka Dot: Parachains and Relay Chain

Polkadot is a Layer 0 blockchain platform designed to enhance interoperability and scalability. Its architecture includes a core Relay Chain that provides shared security and consensus for connected parachains, which are customizable blockchains tailored for specific use cases.
These parachains can communicate with each other using Polkadot’s Cross-Consensus Messaging (XCM) protocol, which allows for trustless, secure cross-chain interactions.
Additionally, bridges are being created to connect Polkadot to external networks such as Ethereum and Bitcoin, further boosting its interoperability capabilities.
Cosmos: Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol

Cosmos aims to establish an “Internet of Blockchains” by facilitating interoperability among independent blockchains.
The Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol is core to its architecture, allowing heterogeneous blockchains to securely and effectively exchange data and tokens.
Cosmos uses the Tendermint consensus engine and the Cosmos SDK to aid developers in creating application-specific blockchains that can interact smoothly within the Cosmos ecosystem.
Avalanche Subnet Architecture
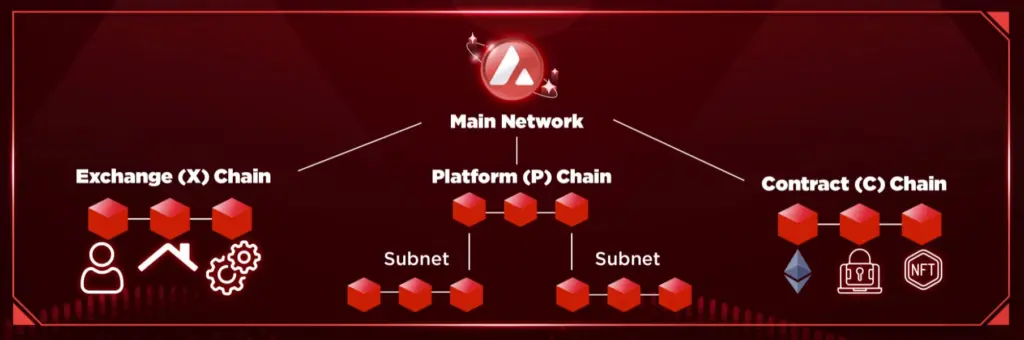
Avalanche introduces the concept of Subnets, which are customizable and interoperable networks that run within the broader Avalanche ecosystem. Each Subnet can establish its own rules, validators, and virtual machines, enabling tailored blockchain deployments.
The Platform Chain (P-Chain) manages Subnet creation and validator coordination, enabling interoperability between Subnets and the main Avalanche network. This architecture allows for scalable and flexible blockchain solutions that cater to a wide range of application requirements.
Layer Zero: Omnichain Interoperability Protocol

LayerZero is an omnichain interoperability protocol that enables seamless communication across different blockchains. It uses Ultra Light Nodes (ULNs) and decentralized oracles to provide secure and efficient message delivery between chains.
LayerZero abstracts the complexities of cross-chain interactions, allowing developers to create decentralized apps that can function across multiple blockchains while maintaining security and performance.
Wormhole: Cross-Chain Messaging Protocol
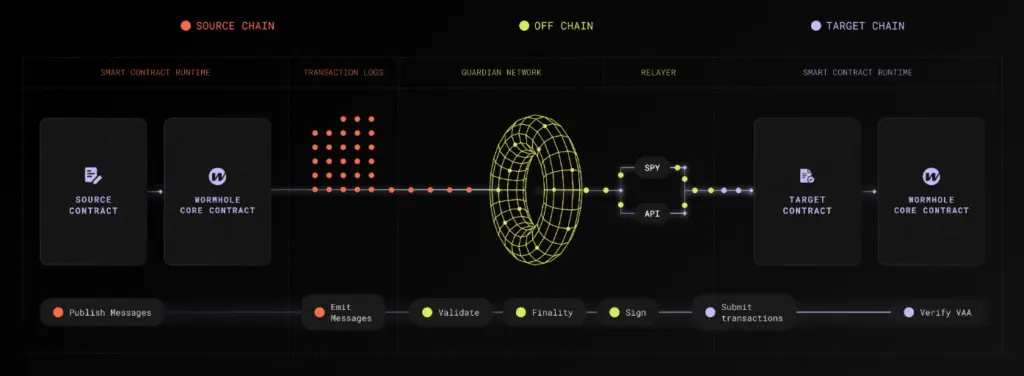
Wormhole is a cross-chain messaging protocol that enables the movement of assets and data between various blockchain networks such as Ethereum, Solana, and Binance Smart Chain.
It uses a network of guardians to monitor and verify events on source chains, allowing for the secure transmission of information to target chains.
Wormhole’s architecture supports a wide range of applications, from token bridges to decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, enhancing interoperability within the blockchain ecosystem.
Chainlink CCIP: Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol
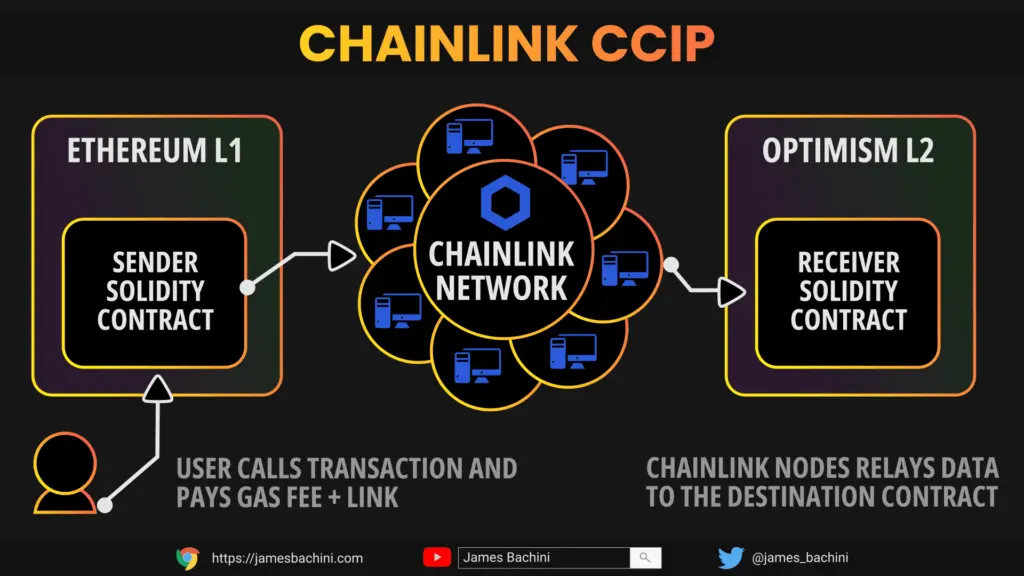
Chainlink’s Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) provides a standardized framework for secure and reliable cross-chain communication.
CCIP leverages Chainlink’s decentralized oracle network, allowing for the transfer of tokens and data between blockchains, facilitating the development of cross-chain decentralized apps.
Its robust security model and broad network support make CCIP a pivotal component in advancing blockchain interoperability.
These leading projects and protocols represent ongoing efforts to achieve seamless interoperability within the blockchain ecosystem. By facilitating secure and efficient cross-chain interactions, they set the foundation for a more integrated and versatile decentralized ecosystem.
Technologies Enabling Interoperable Blockchains
Building interoperable blockchains is critical for creating a cohesive and efficient decentralized ecosystem. Several major technologies facilitate interoperability, with each playing a critical role in enabling seamless communication and asset movement across different blockchain networks.
Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol (IBC)
The Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol is a standardized framework that enables several blockchains to securely communicate and exchange data.
IBC provides smooth cross-chain interactions by managing authentication and data transmission between chains, without the need for trusted intermediaries.
This protocol is essential to ecosystems such as Cosmos, promoting scalability and interoperability across multiple blockchains.
Cross-chain Bridges
Cross-chain bridges are decentralized applications that enable the transfer of assets between multiple blockchain networks. They work by locking or burning tokens on the source chain and creating or unlocking equivalent tokens on the destination chain.
This approach increases token utility and liquidity across platforms, allowing users to connect to multiple ecosystems smoothly.
Oracle and Relayers
Oracles and relayers are key components in blockchain interoperability:
- Oracles: These are services that provide smart contracts with external data, allowing them to respond to real-world events and information. Oracles enable more dynamic and responsive decentralized applications by bridging on-chain and off-chain data.
- Relayers: Enable communication across blockchains by transmitting transaction and event information from one chain to another. This feature is critical for validating cross-chain activities and ensuring the integrity of interconnected blockchain systems.
Smart Contract Standards (e.g, xCall and ERC-20 compatibility)
Standardized smart contract interfaces are critical to maintaining compatibility and interoperability across blockchain networks:
- xCall: This standard enables cross-chain function calls, allowing smart contracts on multiple blockchains to interact directly. xCall facilitates inter-chain communication, supporting the development of more integrated and diverse decentralized applications.
- ERC-20 Compatibility: Maintaining ERC-20 compatibility across blockchains allows tokens to be readily transferred and used within various Ethereum-compatible ecosystems. Standards such as xERC20 and XC-20 broaden this interoperability by allowing tokens to operate seamlessly across several blockchains while adhering to familiar interfaces.
Security Trade-Offs: Trusted vs Trustless Bridges
When implementing cross-chain bridges, it is critical to consider the security implications of various models:
Trusted Bridges: These leverage centralized businesses or intermediaries to facilitate asset transfers between blockchains. While they can provide faster transaction speeds and lower costs, they also pose central points of failure and potential security risks because they rely on trust.
Trustless Bridges: Trustless bridges, which operate without centralized intermediaries, use smart contracts and cryptographic proofs to facilitate asset transfers.
This decentralized technique improves security by reducing trust assumptions, but it may result in more complex implementations and higher operational expenses.
Understanding these trade-offs is critical for selecting a suitable bridging solution that balances security, efficiency, and decentralization based on specific use cases.
Using these technologies, IBC protocols, cross-chain bridges, oracles, relayers, and standardized smart contracts, the blockchain ecosystem gets closer to achieving genuine interoperability.
This interconnected infrastructure is critical for maximizing the potential of decentralized applications and services across several blockchain platforms.
Challenges in Creating a Unified Crypto Ecosystem
While building interoperable blockchains is critical for the future of decentralized finance and apps, a number of significant challenges prevent the actualization of a unified crypto ecosystem.
Security Risks in Cross-Chain Bridges
Cross-chain bridges are critical for interoperability across blockchain networks. They have, however, become prime targets for cyberattacks because of inherent vulnerabilities.
Notably, the Ronin Network, which supports the famous NFT game Axie Infinity, experienced a huge breach where attackers exploited compromised validator nodes to steal about $615 million in Ethereum and USDC.
These incidents highlight the vital need for strong security measures in bridge protocols.
Standardization and Governance Issues
The lack of standardized protocols across blockchain platforms poses a significant barrier to interoperability.
Differences in consensus mechanisms, smart contract languages, and data structures create isolated “value islands,” making seamless interaction challenging.
Establishing uniform standards and governance frameworks is critical for improving cross-chain communication and collaboration.
Scalability of Inter-Chain Protocols
As blockchain adoption increases, the scalability of inter-chain protocols becomes more important. Many existing protocols find it difficult to handle high transaction volumes, resulting in congestion and increased fees.
For instance, low transaction throughput can lead to slower confirmations and poor user experiences. Scalability is essential to support the growing ecosystem of decentralized apps and services.
Economic and Tokenomics Fragmentation
The proliferation of numerous tokens across several blockchains causes economic fragmentation, complicating liquidity and value transfer. This fragmentation presents challenges for users and developers aiming for seamless cross-chain interactions.
Balancing the need for interoperability with the importance of decentralization is a major challenge in cross-chain tokenomics.
Addressing these challenges is critical to the advancement of a cohesive and efficient blockchain ecosystem.
Implementing strong security measures, establishing standardized protocols, increasing scalability, and harmonizing tokenomics are all essential steps toward attaining a unified crypto ecosystem.
The Road Ahead: The Future of Interoperable Blockchains
As blockchain technology advances, the pursuit of interoperability remains a key priority. Emerging trends and innovations are shaping a future where seamless interaction between different blockchain networks will be the norm.
Emergence of Interoperability Hubs
Interoperability hubs are set to play a significant role in the blockchain ecosystem. Platforms such as Polkadot and Cosmos highlight this trend by facilitating communication between different blockchains using relay chains and hubs.
These structures enable a more connected and cooperative decentralized network, which promotes scalability and the development of new cross-chain apps and decentralized finance (DeFi) solutions.
Blockchain Abstraction and User-Centric Interfaces
Chain abstraction is gaining momentum as a means of enhancing the user experience. This method simplifies interactions with multiple blockchains by concealing underlying complexities, allowing people to connect with decentralized apps without requiring extensive technical knowledge.
Chain abstraction lowers entry barriers and facilitates a broad adoption of blockchain technology by providing a unified interface.
Increasing Collaboration Among L1s and L2s
Collaboration between Layer 1 (L1) and Layer 2 (L2) solutions is intensifying to overcome scalability and interoperability challenges.
L2s, such as rollups and sidechains, rely on the security and decentralization of their underlying L1s to provide higher throughput and lower fees.
This symbiotic relationship allows for seamless data and asset transfers between layers, fostering a more efficient and interconnected blockchain ecosystem.
Role of AI and Automation in Cross-Chain Coordination
AI and automation are emerging as important components for managing cross-chain interactions. AI can optimize transaction routing, predict network congestion, and detect anomalies, improving the efficiency and security of cross-chain operations.
Automation streamlines processes such as smart contract execution and data synchronization across blockchains, lowering the risk of human error and increasing system reliability.
Interoperability as the Foundation of Web3 Evolution
Interoperability is fundamental to the realization of Web3, a decentralized, user-centric internet. Interoperability enables seamless communication and value exchange across multiple blockchain networks, facilitating the development of complex, multi-chain applications and services.
This interconnection is critical for driving innovation, improving the user experience, and realizing the full potential of decentralized technology.
The future of interoperable blockchains is defined by the development of interoperability hubs, the implementation of chain abstraction for better user interfaces, increased collaboration between L1 and L2 solutions, and the collaboration of AI and automation for efficient cross-chain coordination.
These advancements collectively facilitate the evolution of Web3, fueling the transition to a more connected and decentralized digital ecosystem.
Conclusion
Interoperable blockchains are no longer a luxury; they are a necessity. As the decentralized ecosystem grows, the ability of different blockchain networks to interact and operate seamlessly becomes critical.
Interoperable blockchains enable the seamless transfer of data and assets across several networks, improving liquidity, scalability, and user experience.
This interconnectedness is vital for the evolution of Web3, allowing for more complex and integrated decentralized apps (dApps) to function across platforms.
By embracing interoperability, we can build a more connected, efficient, and inclusive digital future.
