Ether lost to bugs and user errors has jumped 44% since March 2023, now totaling 913,111 ETH—0.76% of the total supply, says Coinbase exec.
Conor Grogan, head of product at Coinbase, stated that the amount of Ether lost forever due to user error and flaws had reached 913,111 ETH, or around 0.76% of Ether’s current circulating quantity.
Grogan posted the estimate on X on Sunday, pointing out that the Ether lost due to flaws and human mistakes, which currently amounts to about $3.43 billion at current market pricing.
The percentage of ETH lost is significantly greater when 5.3 million ETH have been destroyed since 2021 due to Ethereum Improvement Proposal 1559 (EIP-1559).
According to Grogan, the total amount of Ether lost, including ETH destroyed with EIP-1559, would be around 6.2 million ETH ($23.4 billion), or 5% of Ether’s current supply of 120.7 million.
Since March 2023, Supply Of Lost Ether Has Increased 44%
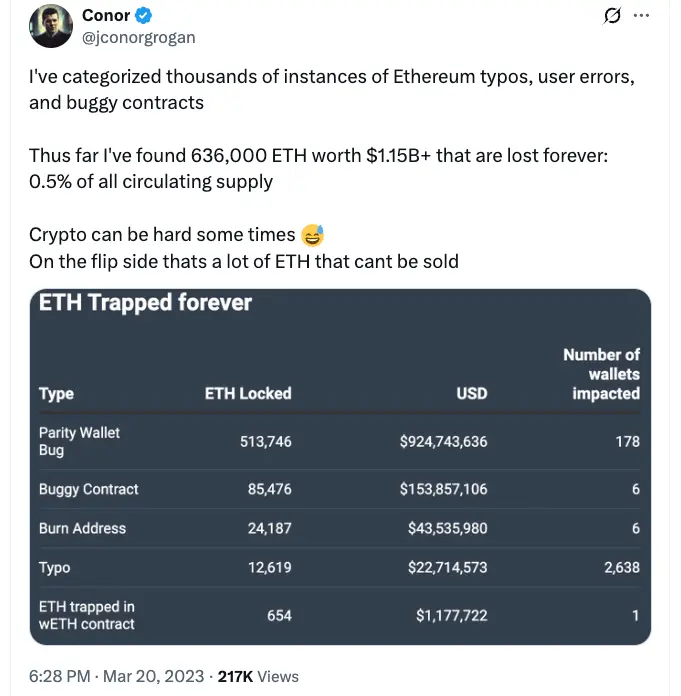
A comparable report from March 2023 states that the quantity of Ether supply lost due to flaws and human error has increased by 44% from the 636,000 ETH recorded at the time.
Despite the increase, the most significant causes of loss have not changed; the most recent study cites the same vital events as Grogan’s March 2023 research identified.
The 306,000 ETH loss resulting from the Web3 foundation‘s Parity Multisig flaw, Quadriga’s 60,000 ETH loss owing to a defective contract, and Akutars’ 11,500 ETH loss in a defective non-fungible token (NFT) mint were all expressly mentioned in both papers.
The transactions to a burn address, which have increased by 1,000 ETH, are the only thing that has changed since then.
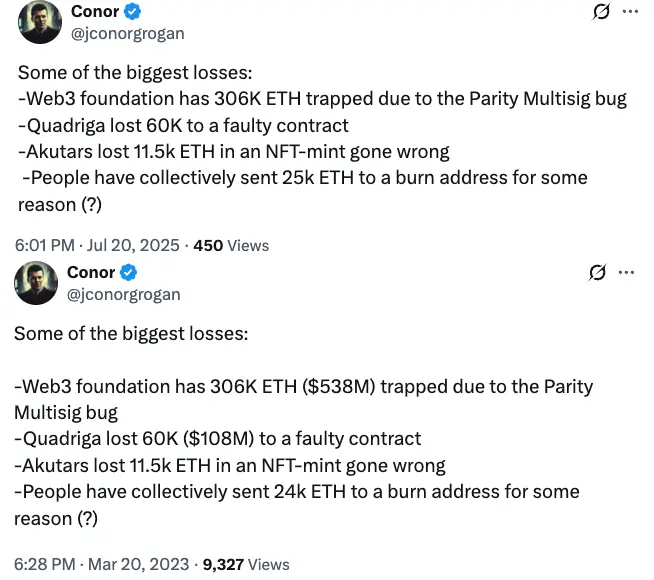
In the most recent report, Grogan stated, “To be clear, this $3.4 billion number significantly undershoots the actual lost/inaccessible ETH amount — it just covers instances where ETH is locked forever.”
“For instance, it doesn’t cover all lost private keys or forgotten items like Genesis wallets,” he continued.
By publication, Cointelegraph had not heard back from Grogan on the leading causes of the spike in ETH supply losses since March 2023.
Ethereum Supply Is Adaptable
Unlike Bitcoin, which has a maximum supply of 21 million coins, ETH has no hard cap on its total supply.
Nevertheless, two key upgrades—EIP-1559 and the Merge—have severely limited the issuance of ETH.
EIP-1559, which was first introduced in August 2021 as part of the London Hard Fork, altered ETH fee system by gradually decreasing the amount in circulation by burning a portion of transaction fees.
After the Merge, which was finished in September 2022, the Ethereum network switched from proof-of-work (PoW) to proof-of-stake (PoS), which led to a sharp decline in the amount of new ETH issued.
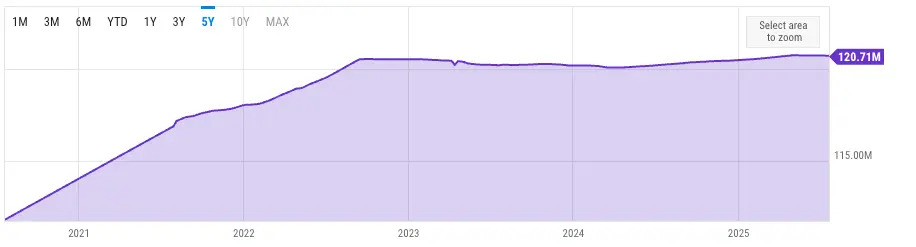
The supply of ETH increased gradually between 2020 and 2022, reaching 120.5 million ETH by September of that year, according to data from YCharts.
After that, the supply fell roughly 0.4% until April 2024 due to continued ETH burns and decreased issuance.
Since then, the supply has gradually increased again, and as of this writing, it stands at about 120.7 million ETH.



