Solana’s Pyth Oracle vs Chainlink highlights a critical decision for developers and investors, emphasizing each oracle’s unique value in the evolving world of DeFi.
Before discussing Solana’s Pyth Oracle vs Chainlink, let’s dive into why decentralized oracles are important for blockchain.
- 1 Table of Contents
- 2 Why Decentralized Oracles are Important for Blockchain
- 3 Chainlink: The Established Oracle Leader
- 4 Solana’s Pyth Oracle: A Newcomer with Potential
- 5 Solana’s Pyth Oracle vs Chainlink
- 6 Decentralization and Security
- 7 Future of Price Feed Oracles in DeFi and Beyond
- 8 Use Cases and Adoption Rates
- 9 Conclusion
Table of Contents
Why Decentralized Oracles are Important for Blockchain
Decentralized oracles are specialized services that connect blockchains to off-chain data sources, allowing smart contracts to receive real-world data in a decentralized manner. Oracles are required as mediators since traditional blockchains cannot access external data directly.
This requirement is heightened in DeFi, and accurate and decentralized price feeds from oracles ensure the safe execution of financial transactions while reducing the possibility of manipulation or reliance on a single source.
Use Cases:
Oracles provides live price data in DeFi lending protocols to calculate loan-to-value ratios and ensure fair liquidation processes. Stablecoins, which rely on oracles to accurately peg their value, and synthetic assets, which replicate real-world assets, both rely largely on decentralized oracles.
Similarly, blockchain-based insurance models use oracle-driven data to provide correct claim verification, demonstrating how oracles support innovation throughout the DeFi ecosystem.
These roles highlight the disparity between Solana’s Pyth Oracle vs Chainlink. As these platforms compete for leadership in providing trustworthy data, they impact the future of decentralized finance, influencing both user trust and the stability of blockchain innovations.
Chainlink: The Established Oracle Leader

Chainlink has become synonymous with decentralized oracle networks, having pioneered solutions for connecting blockchain-based smart contracts to real-world data.
Chainlink, founded in 2017, soon became the go-to oracle solution for developers seeking dependable and secure external data sources, especially in the DeFi sector.
Chainlink has gained partnerships with hundreds of blockchain projects by establishing an early foothold and consistently expanding its technology, including important integrations in Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and beyond.
Technical Structure and Core Technology
Chainlink’s infrastructure is built on a decentralized network of independent nodes that retrieve, validate, and feed external data into smart contracts.
To ensure data reliability and quality, each node operator in the network must stake tokens and maintain a good reputation, which serves as a deterrent to malicious actors and enforces high standards.
The protocol’s multi-layered design includes features such as reputation scoring, which monitors node performance, data aggregation to improve accuracy, and crypto-economic incentives that align node operators’ interests with network reliability.
Chainlink also developed innovative technologies like Chainlink VRF (Verifiable Random Function) for secure randomization in gaming applications and DECO for privacy-preserving oracles.
These advancements have increased Chainlink’s utility beyond price feeds, transforming it into a versatile infrastructure layer in the blockchain ecosystem.
Notable Achievements and Integrations
Chainlink’s partnerships span various industries, including finance, insurance, gaming, and even weather data applications.
Chainlink oracles are used by major initiatives in the DeFi ecosystem, like Aave and Synthetix, to receive secure pricing feeds for collateralized lending and synthetic asset creation.
The protocol’s collaborations with non-blockchain entities, such as Google Cloud and SWIFT, demonstrate its efforts to bridge the traditional and decentralized financial sectors, resulting in a strong framework for real-world data integration across blockchain applications.
When comparing Solana’s Pyth Oracle vs Chainlink, Chainlink’s leadership is distinguished by its maturity, broad integrations, and ongoing innovation.
While Pyth Oracle provides unique, high-frequency data feeds suited for the Solana blockchain, Chainlink’s established multi-blockchain presence and technological maturity set a standard for reliability and security.
Chainlink continues to be the gold standard for developers and investors assessing decentralized oracle solutions, paving the way for a more in-depth look at what emerging oracles like Pyth may offer.
Solana’s Pyth Oracle: A Newcomer with Potential
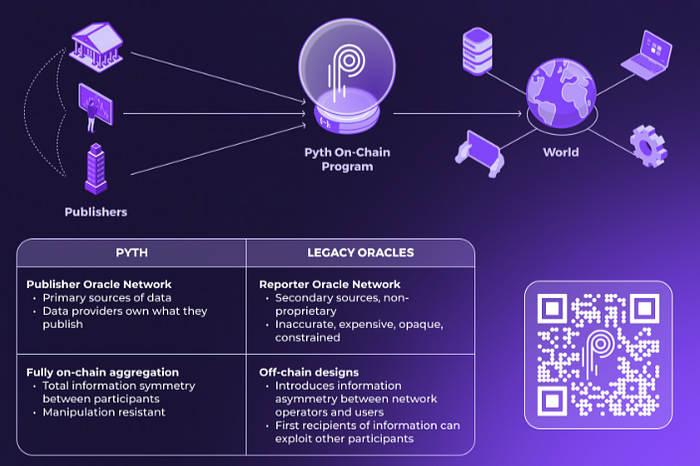
Solana’s Pyth Oracle is an ambitious and unique oracle network designed exclusively for the Solana blockchain, with a significant emphasis on delivering high-speed, low-cost, real-time data.
Pyth developed as part of Solana’s broader effort to build a scalable DeFi ecosystem, aims to offer live, low-latency financial data to blockchain applications, positioning itself as a valuable alternative to more established oracles such as Chainlink.
This emphasis on fast, cost-effective data updates makes it ideal for use cases in fast-moving markets like crypto trading, options, and synthetic asset creation.
Introduction to the Python Network
The Pyth Network has a unique mission: to collect real-world data from reputable data suppliers such as top exchanges, trading firms, and financial institutions.
Pyth aims to provide accurate and near-instantaneous price feeds by taking data directly from these trusted sources, bridging the data flow between off-chain financial markets and on-chain applications.
Unlike traditional oracles, which collect data from several nodes and distribute it in intervals, Pyth’s solution depends on primary sources and on-chain data aggregation to provide price updates at high frequency.
Unique Features and Capabilities
One of Pyth’s key advantages is its integration with Solana’s fast, low-cost blockchain infrastructure.
Solana’s Proof of History (PoH) consensus mechanism enables Pyth to offer time-stamped data with exceptionally low latency, which is crucial for price-sensitive applications such as trading and market-making.
This infrastructure enables Pyth to give market data updates every 400 milliseconds, which is far faster than other Oracle solutions available today, particularly those based on Ethereum or other slower blockchains.
Another distinguishing feature of Pyth is its capacity for data aggregation within the Solana network, which reduces reliance on off-chain intermediaries. Pyth’s data accuracy is improved through direct partnerships with industry leaders who provide high-quality, actionable data.
Pyth, as a decentralized network, also employs on-chain security features, making it more resistant to manipulation while reducing the overhead expenses associated with external Oracle services.
Potential Applications and Ecosystem Impact
As Solana’s DeFi ecosystem expands, Pyth’s high-frequency, low-cost oracle services are expected to play an important role in powering a wide range of applications, including decentralized exchanges (DEXs), automated trading algorithms, and synthetic asset platforms.
Protocols that require precise and timely data, like derivatives platforms and options trading, benefit greatly from Pyth’s infrastructure, which has the potential to increase the efficiency and transparency of Solana’s financial ecosystem.
Furthermore, as Solana attracts developers interested in DeFi and NFT applications, Pyth Oracle’s ability to accommodate low-latency data feeds makes it a critical component for scaling high-volume blockchain applications.
When comparing Solana’s Pyth Oracle vs Chainlink, Pyth stands out as a high-performance newcomer designed specifically for Solana’s unique features.
Whereas Chainlink prioritizes multi-chain operability and a large network of data providers, Pyth focuses on speed and cost-efficiency inside the Solana network, specifically meeting the high-frequency data demands of DeFi applications.
This specialization establishes Pyth as a powerful tool for Solana-based applications, complementing Chainlink’s cross-chain adaptability and security reputation throughout blockchain ecosystems.
Solana’s Pyth Oracle vs Chainlink
The table below compares Pyth Oracle vs Chainlink in terms of data supply, latency, network compatibility, and core strengths:
| Feature | Pyth Oracle | Chainlink |
| Data Collection | Direct data sourcing from high-frequency financial markets and first-party providers | Aggregated data from multiple independent nodes for decentralized verification |
| Delivery Method | Direct, high-speed feeds from primary data sources | Aggregated feeds with consensus verification across nodes |
| Latency | Extremely low latency (~400 ms), leveraging Solana’s high-speed architecture | Higher latency, dependent on the blockchain network used (e.g., slower on Ethereum) |
| Blockchain Compatibility | Primarily designed for Solana | Multi-chain compatible (e.g., Ethereum, BSC, Polygon) |
| Network Speed | Optimized for rapid updates due to Solana’s Proof of History (PoH) | Dependent on host blockchain speed; slower on high-latency chains |
| Core Strengths | Real-time data for DeFi applications; ideal for trading, derivatives, and high-speed markets | Broad ecosystem support with decentralized validation; strong security and reliability |
| Best Use Cases | Low-latency financial data feeds, Solana-based DeFi, trading protocols | Cross-chain compatibility, diverse applications (DeFi, NFTs, insurance, gaming) |
This table compares the distinct technical aspects that distinguish Pyth Oracle and Chainlink, as well as how they address specific needs in the decentralized finance and broader blockchain space.
Decentralization and Security
Security Models: Chainlink and Solana’s Pyth Oracle take distinct approaches to decentralization and data integrity. Chainlink has long been known for its strong decentralized methodology, which validates data flows through a vast network of independent, incentivized node operators.
Chainlink’s broad network has made it extremely reliable, as it distributes trust over multiple nodes, limiting the possibility of single points of failure or data manipulation.
Solana’s Pyth Oracle, on the other hand, prioritizes real-time accuracy and reliability while maintaining its security. It collects data directly from financial institutions and uses Solana’s high-speed architecture to provide low-latency updates, which are crucial for fast-moving DeFi applications.
Risks and safeguards: Each protocol includes measures to ensure data integrity and prevent manipulation. Chainlink’s decentralized architecture incorporates data gathering from numerous sources, which is then consensus-validated to find and minimize inaccuracies.
Solana’s Pyth Oracle approach entails sourcing from select high-trust sources, which results in faster data but a distinct risk structure.
Solana’s Pyth Oracle approach aims to blend speed and selective decentralization, eliminating attack vectors through partnerships with reliable financial sources, whereas Chainlink’s security approach is based on decentralized validation across its vast network.
In the comparison of Solana’s Pyth Oracle vs Chainlink, both offer distinct security structures. Chainlink has a wide node distribution, and Solana’s Pyth Oracle has high-speed, high-reliability data sources to cater to diverse needs within the DeFi ecosystem.
Future of Price Feed Oracles in DeFi and Beyond
- Growth Projections: Decentralized oracles, such as Solana’s Oracle Pyth and Chainlink, are projected to become increasingly popular as DeFi, NFT markets, and real-world asset tokenization expand.
As DeFi protocols get more complex, the demand for reliable, low-latency data feeds capable of handling high-frequency transactions grows. The predicted increase in decentralized blockchain applications, spanning from finance to supply chain management, emphasizes the significance of reliable Oracle solutions.
Solana’s Pyth Oracle low-latency design, customized to Solana’s high-speed environment, could make it suitable for high-frequency trading and DeFi applications. Meanwhile, Chainlink’s multi-chain flexibility ensures that it remains relevant across several platforms.
- Potential Industry Impact: As both oracles improve to suit the needs of DeFi and beyond, they could play a critical role in enabling more secure, transparent, and efficient decentralized systems.
Pyth and Chainlink are not just influencing the DeFi scene, but they may also have an impact on other industries, such as insurance, synthetic asset creation, and even traditional finance integrations.
Their developments may accelerate the adoption of blockchain technology in real-world applications by delivering reliable, timely data feeds required for smart contract operation.
Solana’s Pyth Oracle vs. Chainlink discusses how these oracles are poised to shape the future of decentralized finance by establishing standards that could redefine real-time data applications across blockchain ecosystems and beyond.
Use Cases and Adoption Rates
Current Adoption and Partnerships: Chainlink and Solana’s Pyth Oracle have developed significant partnerships, demonstrating their attraction and use across blockchain ecosystems.
Chainlink has established itself as the preferred oracle for various DeFi projects, including major protocols such as Aave, Synthetix, and Compound, owing to its multi-blockchain compatibility and high degree of trust in DeFi marketplaces.
Its various relationships demonstrate its strong position in the industry, as developers frequently rely on Chainlink for dependable and secure data flows across Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and other networks.
Solana’s Pyth Oracle, while relatively new, is gaining traction, particularly in its high-speed ecosystem.
Pyth partners with financial heavyweights such as Jump Trading, Virtu, and other renowned institutions to receive real-time financial data directly from reputable sources, making it an enticing solution for applications that require rapid, accurate data.
The unique approach not only reinforces its adoption within Solana but also shows its potential for scaling into other ecosystems as demand for low-latency price feeds increases.
- Future Prospects: Chainlink’s success depends on its ability to stay blockchain-agnostic while expanding its data oracle services beyond DeFi into broader real-world utilization.
With developments like Chainlink 2.0, which promises to improve data privacy and scalability, the protocol is poised to expand its reach in DeFi and beyond.
Meanwhile, Solana’s Pyth Oracle high-frequency data feeds are especially appealing to trading and financial applications that benefit from Solana’s fast transaction speeds.
As it evolves, Pyth may consider expanding its infrastructure to other high-speed blockchains, capturing use cases that require both speed and direct data sourcing.
When assessing Solana’s Pyth Oracle vs. Chainlink, real-world uses highlight their various approaches: Chainlink’s comprehensive cross-chain capabilities and Pyth’s specialized high-speed data delivery for financial markets.
Conclusion
As the DeFi environment evolves, both Solana’s Pyth Oracle and Chainlink are expected to play critical roles in shaping decentralized finance and beyond.
When deciding which solution is best for your needs, you should examine the qualities of both Chainlink’s established, network-driven security model and Pyth’s speedy data delivery from reputable sources.



