Data availability layers serve as the foundation for secure information flow; these specialized layers ensure that all required data is published, verifiable, and accessible across the network.
In this article, we explore the role of data availability layers in next-gen blockchains and how they influence scalability, security, and ecosystem expansion for decentralized apps.
What Are Data Availability Layers?
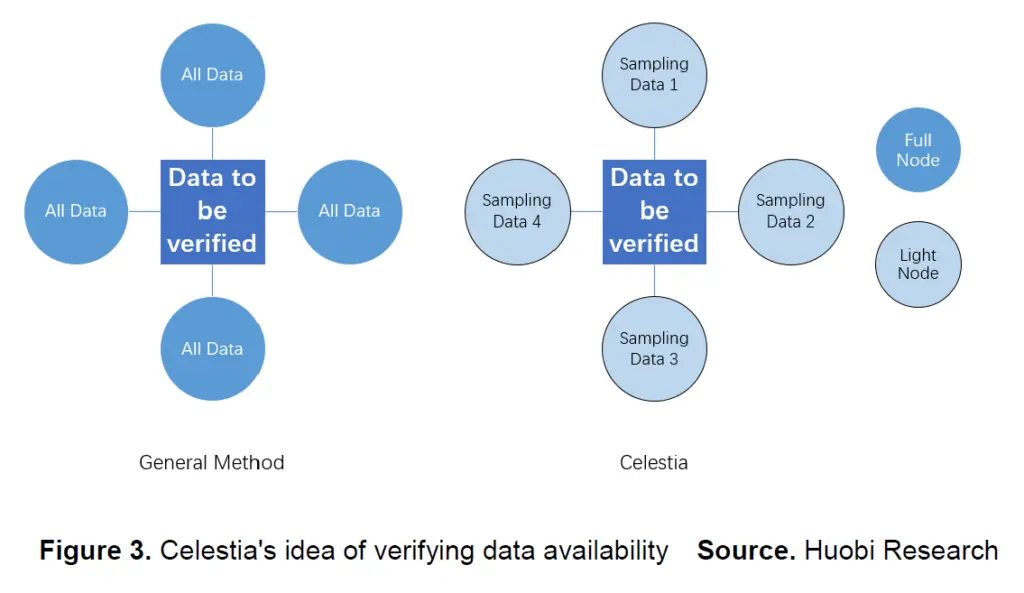
In blockchain systems, data availability (DA) layers are specialized mechanisms designed to guarantee that all transaction data is published and accessible to all network participants.
Simply put, a data availability layer ensures that no crucial information is concealed, allowing validators, nodes, and users to validate transactions independently of a centralized authority.
The function of data availability layers extends beyond storage; they separate execution from data management. While smart contracts and rollups execute transactions, the data availability layer distributes and secures the underlying data.
This separation is especially important for rollup and sharded blockchains, which rely on external data availability assurances to ensure security and prevent malevolent actors from concealing fraudulent transactions.
Key Features of Blockchain Data Availability Systems:
- Redundancy: Data is dispersed across multiple nodes to avoid loss or manipulation.
- Verifiability: Participants can use cryptography to confirm that data has been properly published.
- Fault Tolerance: Even if some nodes fail, the network continues to provide reliable access to data.
By addressing the scalability trilemma, data availability layers allow blockchains to execute more transactions while maintaining decentralization or trust.
Whether for rollup data integrity or sharding support, data availability layers are rapidly becoming the foundation of next-gen blockchain infrastructure.
Challenges Solved by Data Availability Layers
Blockchains face a fundamental challenge: how to scale while maintaining security and transparency. This is where data availability layers come in, solving some of the industry’s most urgent concerns.
1. Scalability Bottlenecks
Traditionally, each blockchain node had to download and store all transaction data. As usage increases, this design becomes a bottleneck, slowing networks and increasing the cost of full node participation.
Data availability layers solve this by separating execution and data storage. Instead of overloading each node, they ensure that data is published, verifiable, and retrievable as needed. This enables higher throughput for rollups and sharded ecosystems.
2. Security and Fraud Prevention
Without reliable data availability, malicious actors could attempt data withholding attacks, concealing information required to verify transactions. This would allow invalid rollup proofs to pass through undetected.
Data availability layers mitigate this risk by ensuring that all transaction data is broadcast and verifiable, hence maintaining the trustless security that blockchains promise.
3. Cross-Shard Data Consistency
As networks adopt multi-shard architectures, applications frequently span many shards. Data availability layers ensure that transaction data is consistently available across shards, reducing fragmentation and facilitating smooth interoperability between different parts of the blockchain.
4. Real-world Solutions
Projects such as Ethereum rollups (Optimism, Arbitrum) rely on Ethereum’s data availability layer to protect their systems.
Meanwhile, Celestia is pioneering modular data availability networks, designed to provide scalable, verifiable data availability across different rollups and application-specific blockchains.
In essence, data availability layers eliminate scalability constraints, strengthen security, and enable cross-chain consistency, making them a critical component of next-gen blockchain infrastructure.
Types of Data Availability Solutions
As next-gen blockchains evolve, several data availability (DA) solutions emerge to balance scalability, security, and decentralization. Understanding these approaches reveals how networks accomplish efficient and reliable data access.
1. Full Nodes vs Light Clients
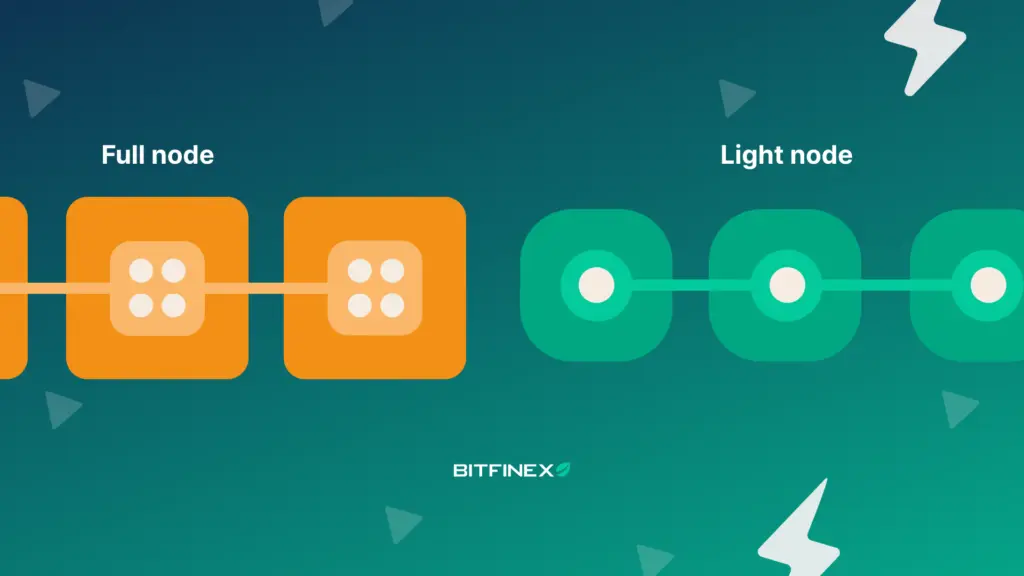
Traditional blockchains, full nodes to download and store all transaction data, ensuring maximum security and verifiability. However, this requires significant storage and bandwidth requirements, limiting involvement to well-funded entities.
In contrast, light clients only store block headers and rely on cryptographic proofs to verify data availability. While more lightweight, they sacrifice some independence by relying on advanced verification techniques such as sampling.
2. DA Layers as Separate Protocols
A modular approach introduces dedicated DA layers that specialize in publishing and securing transaction data, freeing execution layers from storage burdens.
- Celestia pioneered this model, providing scalable DA for rollups and sovereign chains via data availability sampling.
- Polygon Avail offers high-throughput DA with robust redundancy for Web3 applications.
- EigenLayer uses Ethereum’s validator set to protect middleware, including DA services, through a “restaking” technique.
These specialized protocols lower developer expenses while ensuring verifiable access to blockchain data.
3. Erasure Coding and Sampling Techniques
To enable trustless verification without requiring every node to store entire blocks, data availability layers employ erasure coding and data availability sampling (DAS).
Erasure coding fragments transaction data with redundancy, allowing for full reconstruction even after a partial retrieval.
Sampling allows light clients to randomly verify small parts of data. If there are enough samples, the whole dataset is highly likely to be available.
Together, these techniques enable blockchains to scale while keeping verification decentralized and efficient.
Comparative Snapshot (Simplified)
| Solution | Throughput | Verification | Decentralization | Example Use Case |
| Full Nodes | Low–Medium | Strong | High (resource-heavy) | Legacy chains |
| Light Clients | Medium | Moderate (with sampling) | High (accessible) | Mobile/Web3 apps |
| DA Layers | High | Strong (erasure coding + DAS) | High (modular) | Rollups, DAOs |
By combining these solutions, the blockchain ecosystem is moving toward scalable yet secure DA models, essential for powering the next wave of decentralized applications.
Impact on Next-Gen Blockchains
The integration of data availability layers is transforming how next-gen blockchains achieve scalability, security, and usability. By separating execution from data storage, data availability layers enable performance gains that were previously limited by traditional architectures.
1. Rollups and Layer-2 Scaling
One of the most apparent impacts is on rollups, Ethereum’s preferred scaling mechanism. Rollups bundle transactions off-chain but rely on data availability layers to send data back to the main chain for verification.
This model allows for faster transactions, lower gas fees, and trustless security. Solutions such as Optimism and Arbitrum are already utilizing data availability innovations to boost throughput, while emerging rollup ecosystems rely on specialized DA protocols like Celestia and Polygon Avail.
2. Interoperability Across Chains
Data availability layers also play an important role in facilitating interoperability. By standardizing how transaction data is published and verified, multiple chains and Layer 2 networks can share a common data foundation.
This enables cross-chain decentralized apps (dApps), such as multi-chain DeFi platforms or interoperable NFT marketplaces, to operate securely without duplicating storage efforts.
3. Developers and Users Benefits
For developers, data availability layers mean cheaper node costs because they no longer have to store all transaction data locally.
For users, this means more reliable access to blockchain data, faster application responsiveness, and increased trust in decentralized ecosystems.
Furthermore, higher throughput capacity ensures smoother scaling as demand for decentralized finance, gaming, and AI-driven Web3 services rises.
In short, the role of data availability layers in next-gen blockchains is both technical and transformative.
They lay the foundation for the future of scalable, interoperable, and user-friendly Web3 infrastructure, ensuring that both developers and users benefit from speed, cost-efficiency, and security.
Risks and Considerations
While data availability layers enable scalability and efficiency, they also pose unique risks and trade-offs that next-gen blockchains must address.
1. Data-Withholding Attacks
One of the major risks is the possibility of data withholding attacks, where malicious actors publish commitments without making the underlying transaction data available. This reduces rollup validity and user trust.
Erasure coding, data availability sampling (DAS), and fraud-proof mechanisms are instances of mitigation strategies that allow light clients to probabilistically verify data availability without storing everything.
2. Network Latency and Consensus Trade-Offs
Adding a dedicated data availability layer can increase network latency, especially if nodes need to coordinate across multiple layers. Consensus protocols that maximize availability sometimes trade speed, resulting in longer confirmation times.
Next-gen designs aim to balance low-latency throughput with resilient redundancy, but performance will differ with solutions like Celestia, Polygon Avail, and EigenLayer.
3. Adoption and Integration Hurdles
Adoption is not automatic for developers or enterprises. Integrating DA solutions into existing Layer 1 and Layer 2 ecosystems requires technical knowledge and a learning curve for new SDKs, APIs, and validation models.
Furthermore, ecosystem fragmentation could slow widespread adoption until interoperability standards mature.
The role of data availability layers in next-gen blockchains presents both opportunities and risks.
Addressing security vulnerabilities, eliminating latency trade-offs, and lowering adoption barriers will be crucial to ensuring data availability solutions fulfill on their promise as the foundation of scalable, secure Web3 infrastructure.
Real-World Implementations and Case Studies
The role of data availability layers in next-gen blockchains is no longer theoretical. Several live protocols and pilots are already changing how decentralized ecosystems’ scalability, reliability, and security.
Celestia: Pioneering Modular Data Availability
Celestia launched as the first dedicated data availability layer for rollups and modular blockchains. By separating consensus and execution, developers can deploy sovereign rollups without having to depend on Ethereum or other Layer 1s for data storage.
Celestia relies on data availability sampling (DAS), which allows light clients to efficiently verify large blocks. Early adoption by rollup ecosystems indicates that modular data availability can reduce costs and increase throughput while maintaining verifiability.
Polygon Avail: Enterprise-Ready Data Availability Layer
Polygon Avail takes a distinct approach, focused on enterprise-grade data availability solutions. It offers a high-throughput, fault-tolerant data availability network that supports Ethereum rollups, sidechains, and Web3 applications that require reliable data publication.
Its architecture emphasizes redundancy and fault tolerance, making it appealing to enterprises seeking scalability without compromising compliance or security guarantees.
EigenLayers and Emerging Protocols
EigenLayer introduces restaking and staking-as-a-service as methods for securing data availability networks and other middleware. Validators can use their ETH to provide security to data availability services, lowering economic risks like data withholding.
This technique also encourages adoption by aligning security to Ethereum’s validator set. Other emerging protocols, such as Near DA initiatives and DA modules within zkSync ecosystems, indicate a growing market of specialized data availability solutions.
Lessons Learned
These implementations highlight clear performance and security trade-offs. Celestia shows how modular data availability can provide developer flexibility, but it also introduces cross-layer coordination complexity.
Polygon Avail shows enterprise adoption potential, though interoperability remains a barrier. EigenLayer shows promise in terms of aligning incentives, but its success depends on Ethereum restaking.
Collectively, these case studies demonstrate how data availability layers are becoming the backbone of scalable Web3 infrastructure, balancing security, throughput, and cost-efficiency for next-gen blockchains.
Future Outlook
The next 12-24 months will be defined by modular blockchains, where execution, consensus, and data availability (DA) are specialized layers. Expect DA-powered cross-chain rollups to emerge, allowing dApps to span multiple Layer2s while maintaining security via a shared DA backbone.
This will speed up DeFi and NFT scaling, allowing for cheaper mints, higher TPS markets, and cross-ecosystem liquidity without sacrificing verifiability.
Predictions
Predictions: Data availability layers layers will gain traction in L2s, sharded L1s, and hybrid appchains.
General-purpose rollups will increasingly externalize data availability to cut fees and increase throughput, while enterprise and gaming chains adopt data availability to ensure predictable performance and auditability.
Sharded L1s will pair native shards and external DA to improve cross-shard data consistency. Meanwhile, restaking-secured DA services will mature, increasing the security budget for middleware and reducing data-withholding risks.
Developer Ecosystem Growth
This flywheel will be reinforced as the developer ecosystem grows. Expect more robust SDKs, node toolchains, and light-client libraries, making data availability integrations essentially “one-line imports.”
Turnkey rollup stacks will include pluggable DA modules (e.g., Celestia/Avail/Ethereum blobs), erasure-coding utilities, and data availability sampling (DAS) primitives for mobile and browser clients.
Observability will improve via data availability explorers, sampling dashboards, and cost simulators, helping teams tune latency, redundancy, and fees.
The role of data availability layers in next-gen blockchains will shift from optional optimization to baseline architecture, powering scalable, interoperable networks where developers ship faster, users pay less, and security is verifiable from end to end.
Conclusion
The role of data availability layers in next-gen blockchains is central to building scalable, secure, and future-ready networks.
By ensuring that transaction data is reliably accessible to all nodes, DA layers eliminate scalability bottlenecks, protect against data-withholding attacks, and enable seamless cross-chain interoperability.
From supporting rollups to powering modular blockchain ecosystems, DA has become an essential part of Web3’s growth.
Now is the moment to monitor these protocols, experiment with modular designs, and embrace DA as a key component of next-gen blockchain development.



