Forex market dynamics are shifting with the rise of CBDCs. Explore how CBDCs could disrupt currency trading, reduce costs, and reshape global financial systems.
- 1 Understanding the Forex Market: “What is the Forex Market and Why It Matters?”
- 2 The Rise of Central Bank Digital currencies (CBDCs)
- 3 How CBDCs Could Disrupt the Forex Market
- 4 Challenges of Implementing CBDCs in the Forex Market
- 5 CBDCs in Action: Transforming the Forex Market
- 6 The Future of Forex Market with CBDCs
- 7 Conclusion
Understanding the Forex Market: “What is the Forex Market and Why It Matters?”
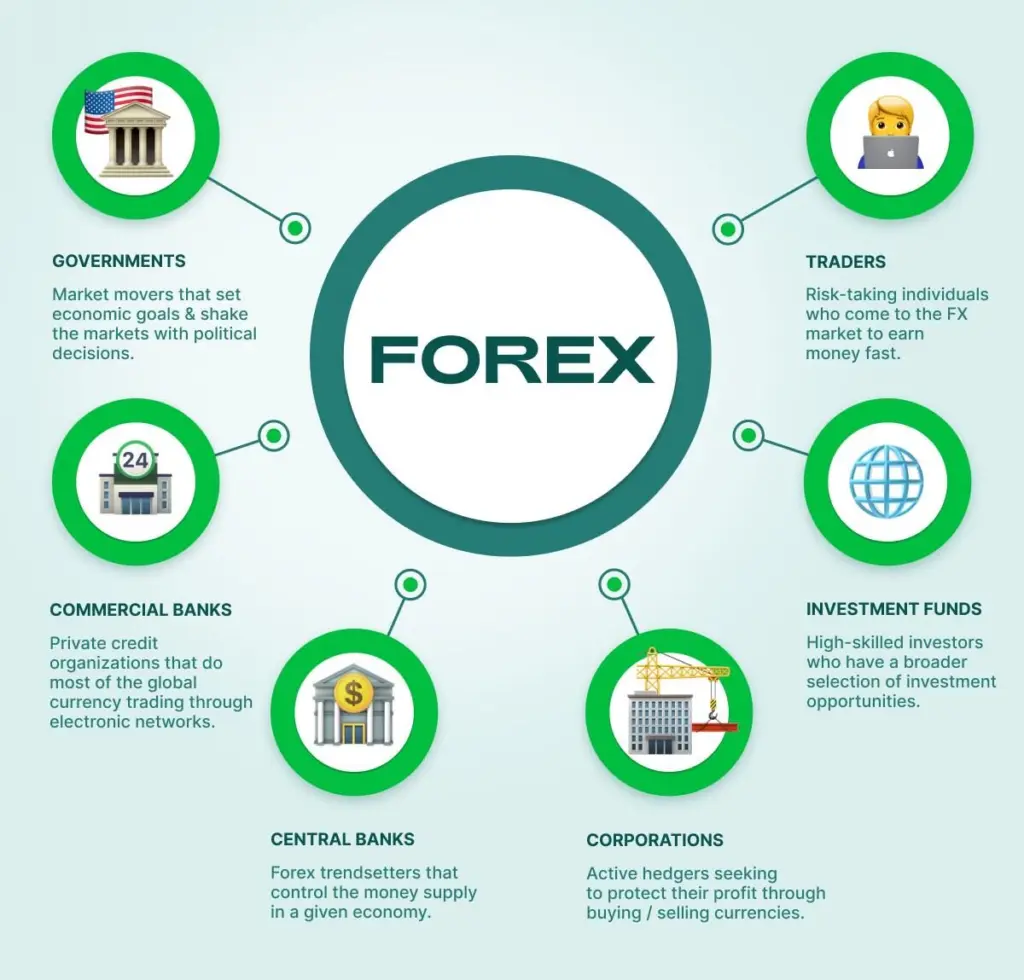
The foreign exchange (Forex) market is the world’s largest financial market, with a daily trading volume of more than $7.5 trillion. It enables the exchange of currencies at agreed-upon prices, making it a cornerstone for global economic activities.
It operates around the clock and provides liquidity, stability, and infrastructure for cross-border transactions between corporations, governments, and investors.
Major Functions of the Forex Market:
Facilitating International Trade and Investment: The Forex market facilitates international trade and investment by enabling businesses to exchange currencies for importing and exporting products and services. This improves global trade flows and increases economic interdependence.
- Determining Exchange Rates: Forex trading sets exchange rates, which influence the cost of goods, export competitiveness, and investment decisions globally. Interest rates, inflation, and geopolitical conditions influence these rates.
- Hedging against Currency Risks: Forex instruments are used by businesses and investors to manage exchange rate volatility, ensuring predictability in costs and returns.
- Enabling Economic Growth: The Forex market promotes global economic growth by attracting foreign investment due to its efficiency and transparency.
The Forex market acts as a foundation for global trade and financial stability. Its efficiency ensures that businesses and individuals can access and exchange currencies in real-time, which is essential for today’s interconnected economy.
The Rise of Central Bank Digital currencies (CBDCs)

Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are digital equivalents of a country’s fiat currency that the central bank issues and regulates. CBDCs, unlike cryptocurrencies, are fully centralized and operate as legal tender.
They symbolize the digital evolution of money and are created to update traditional financial systems while maintaining control over monetary policies.
Main Features of CBDCs:
- Digital Fiat Equivalent: CBDCs serve as a digital equivalent to physical cash backed by the issuing central bank.
- Centralized Control: Central banks control CBDCs, unlike decentralized cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. This enables governments to monitor transactions and oversee monetary policies.
Types of CBDCs:
- Wholesale CBDCs: Financial institutions use them for large-scale transactions with the goal of streamlining interbank settlement.
- Retail CBDCs: Designed for the general population, they serve as digital cash for everyday transactions.
- Hybrid Models: Combine characteristics from wholesale and retail systems to increase usability.
Examples of CBDC initiatives:
- China’s Digital Yuan (e-CNY): Since 2014, the country has been pioneering trials for digital currency in internal and international trade.
- European Digital Euro: Designed to improve payments within the European Union.
- The Bahamas’ Sand Dollar: The world’s first officially launched CBDC in 2020, targeted at financial inclusion.
Implications for Currency Exchange:
CBDCs can modernize systems by facilitating faster and more cost-effective transactions, particularly in cross-border trade.
They eliminate reliance on intermediaries such as SWIFT while providing more transparency and security. However, the centralized approach raises concerns about data privacy and government overreach.
This transformation has the potential to change how global financial systems operate, making CBDCs an important step toward modernizing the global economy.
How CBDCs Could Disrupt the Forex Market
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) have the potential to fundamentally disrupt the Forex market by altering the processes of currency trading and exchange rates. Here are the main ways CBDCs could reshape the Forex market:
Streamlining Currency Exchange
CBDCs are digital representations of fiat currencies issued by central banks that enable more direct and efficient currency exchange.
CBDCs, as opposed to traditional fiat currencies that rely on intermediaries like banks and payment processors, could enable near-instantaneous settlements, lowering costs and enhancing efficiency for cross-border transactions.
The Impact on Exchange Rates
If a country’s CBDC is widely adopted both domestically and internationally, it may affect the demand for that currency in the Forex market.
For example, the demand for a well-managed CBDC with strong economic backing may cause significant fluctuations in exchange rates, increasing volatility and potentially reshaping traditional currency dominance.
Reduction of Intermediaries
CBDCs could bypass the correspondent banking system and other traditional financial intermediaries in Forex trading. This could result in disintermediation, simplifying currency trading processes, and potentially challenging existing financial infrastructures.
Increased Competition Among Currencies
CBDCs may increase competition among national currencies in global markets. Investors and traders may prefer to own CBDCs from nations with stable economies and sound monetary policies, thereby marginalizing weaker currencies and reshaping global capital flows.
Opportunities for New Financial Products
CBDCs could open up opportunities for innovative financial products and trading tactics in the Forex market. Traders may have access to a broader selection of digital currencies with cheaper transaction fees, promoting increased market liquidity.
Monetary Policy and Surveillance
CBDCs give central banks more direct control over the money supply, which could enable unconventional monetary policies like programmable interest rates. However, concerns about surveillance and privacy could deter adoption among Forex market participants.
CBDCs have significant potential benefits, but challenges such as interoperability, regulatory compliance, and economic dependency on dominant CBDCs remain critical issues for the Forex market.
As CBDCs evolve, their impact on the Forex market will be determined by their adoption, design, and the regulations that govern their use. Forex traders and policymakers must be up to date in order to successfully adapt to these changes.
Challenges of Implementing CBDCs in the Forex Market
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) have transformative potential for the Forex market, but their implementation is plagued with challenges and risks. The following are the main challenges of implementing CBDCs in the Forex market:
- Interoperability Issues
- Regulatory Complexity
- Geopolitical Risks
- Privacy & Security Concerns
- Economic Risks to Small Economies
- Impact on Forex Brokers
Interoperability Issues
One of the most critical challenges for CBDCs in the forex market is ensuring the seamless exchange of currencies issued by different countries.
CBDCs built on siloed platforms or blockchain systems may encounter compatibility issues, complicating cross-border transactions. A lack of global standards exacerbates this issue, potentially fragmenting the forex market instead of unifying it.
Regulatory Complexity
CBDCs require strong regulatory frameworks to oversee their issuance and usage, particularly in the forex market. Conflicting regulations across jurisdictions can result in inefficiencies.
Countries that do not align on regulatory standards may have difficulty in accomplishing seamless international transactions.
Impact on Forex Brokers
The traditional forex trading ecosystem is primarily reliant on brokers and interbank systems.
With CBDCs enabling direct peer-to-peer or central bank-to-bank payments, intermediaries could experience less demand for their services, affecting traditional business models and potentially decreasing the sector.
Geopolitical Risks
Countries with powerful CBDCs, such as China’s e-CNY or a potential US digital dollar, could gain disproportionate influence in global forex markets.
Smaller countries and their currencies may become marginalized, increasing their reliance on larger economies. This uneven playing field could intensify existing geopolitical tensions.
Privacy & Security Concerns
CBDCs, unlike cash, give central banks unprecedented transparency into financial activities, causing concerns about monitoring and data exploitation.
The lack of anonymity could reduce trust among forex traders and participants. Cybersecurity hazards, including hacking and data breaches, are a significant threat to financial stability.
Economic Risks to Small Economies
Smaller economies may struggle to compete with larger nations’ CBDCs, resulting in lower demand for their fiat currencies in forex trading. This move could reduce the value and usefulness of weaker currencies in the global economy.
While CBDCs promise to modernize and simplify currency trading, their application in the forex market presents significant challenges.
Addressing these risks will require collaboration among central banks, regulators, and private institutions to create standards, improve interoperability, and ensure security.
Without these precautions, CBDCs might disrupt the forex market in ways that worsen existing inefficiencies and inequality rather than fix them.
CBDCs in Action: Transforming the Forex Market
Project mBridge: Multi-CBDC Collaboration
Project mBridge, led by the BIS Innovation Hub and involving central banks from China, the UAE, Hong Kong, and Thailand, highlights CBDCs’ transformative potential in foreign exchange.
This multi-CBDC platform, powered by distributed ledger technology (DLT), enables real-time cross-border payments and forex transactions. The project aims to cut costs, increase speed, and address inefficiencies in traditional interbank systems.
It has completed many real-world pilots and reached the minimum viable product stage in 2024, paving the way for broader adoption.
China’s Digital Yuan (e-CNY): Regional Impact
China’s e-CNY has a significant impact on the exchange of Asian currency. China aims to challenge traditional mobile payment systems’ dominance and promote interoperability by integrating the digital yuan into platforms such as Alipay and WeChat.
The e-CNY has been used for international trade and cross-border transactions with neighboring regions, aligning with China’s goal of boosting the yuan’s participation in global markets.
The Digital Euro: Promoting Intra-EU Forex
The European Central Bank’s Digital Euro project aims to streamline multi-currency transactions across the EU. The initiative’s goal is to reduce transaction costs and increase liquidity for intra-European trade by establishing a centralized digital currency.
This method might considerably influence the forex market by lowering reliance on non-EU currencies such as the US dollar.
These real-world applications show how CBDCs are not simply theoretical innovations but also actual tools for modernizing the forex market. CBDCs are shaping a new global currency landscape by providing faster, cheaper, and more transparent transaction mechanisms.
The Future of Forex Market with CBDCs
The rise of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) is set to revolutionize the forex market, ushering in a new era of innovation and efficiency in currency trading.
Speculations About Replacing Traditional Forex Systems
CBDCs provide a state-backed alternative to traditional fiat currencies, with benefits such as fast settlement and more transparency.
CBDCs have the potential to simplify forex trading by enabling real-time, peer-to-peer transactions, unlike the existing system, which relies on intermediaries and experiences delays.
The development has the potential to lower costs and increase liquidity in the forex market, challenging the dominance of traditional trading platforms such as SWIFT.
Furthermore, the programmability of CBDCs enables automatic exchange processes, minimizing reliance on speculative trading tactics and stabilizing currency swings.
Predictions for Global Adoption
Currently, more than 130 countries are exploring or piloting CBDCs, representing 98% of global GDP. Major players such as China’s e-CNY and the European Central Bank’s Digital Euro demonstrate the growing momentum for adoption.
These innovations have the potential to expedite cross-border trade integration, particularly within regional blocs such as the EU and ASEAN.
Experts expect that CBDCs will become widespread within the next decade, with financial institutions gradually integrating these digital currencies into FX systems.
Smaller economies may also use regional or worldwide CBDCs to avoid traditional fiat dependence and level the global financial playing field.
Decentralized Forex Platforms Leveraging CBDCs
The emergence of decentralized FX platforms could parallel the adoption of CBDCs. Blockchain-powered platforms may allow users to trade CBDCs directly with low transaction fees, bypassing traditional brokers.
Such innovations have the potential to democratize the forex market, drawing a broader user base while posing challenges to traditional forex intermediaries.
To succeed in this space, decentralized systems leveraging CBDCs must solve issues such as regulatory compliance, cybersecurity, and interoperability among different national CBDCs.
CBDCs have the potential to transform the forex market by increasing efficiency, lowering costs, and ensuring stability.
While challenges such as regulatory obstacles and geopolitical risks persist, the adoption of CBDCs is likely to transform currency trading in the future decade, creating a more inclusive and dynamic global financial space.
Conclusion
As the adoption of CBDCs accelerates, their effect on the Forex market will be dependent on careful international collaboration to standardize technologies and regulations.
This era of digital currencies has the potential to redefine currency sovereignty and international trade, making the Forex market more dynamic and complex.
Stakeholders must carefully navigate this change to maintain a balanced and inclusive global financial future.