The Federal and Treasury plan to amend the Bank Secrecy Act’s “money” definition to include digital assets and cryptocurrencies in reporting requirements.
Leading US federal agencies are working together to redefine “money” and impose stricter reporting regulations on financial institutions regarding local and international Bitcoin transactions.
On August 16, the US Department of the Treasury released its semiannual regulatory agenda, outlining a future federal effort to level the regulatory playing field for traditional fiat currency and cryptocurrencies.

The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network and the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System intend to update the definition of “money” as it is used under the Bank Secrecy Act.
For Reporting Purposes, Treating Cryptocurrency as Money
As stated on the agenda:
“The agencies (FRS and FinCEN) intend that the revised proposal will ensure that the rules apply to domestic and cross-border transactions involving convertible virtual currency, which is a medium of exchange (such as cryptocurrency) that either has an equivalent value as currency or acts as a substitute for currency, but lacks legal tender status.”
The plan, however, would also include digital assets with legal tender status, such as digital currencies issued by central banks, under the reporting obligation.
Subject to approval, the final notice of proposed regulation is scheduled for September 2025.
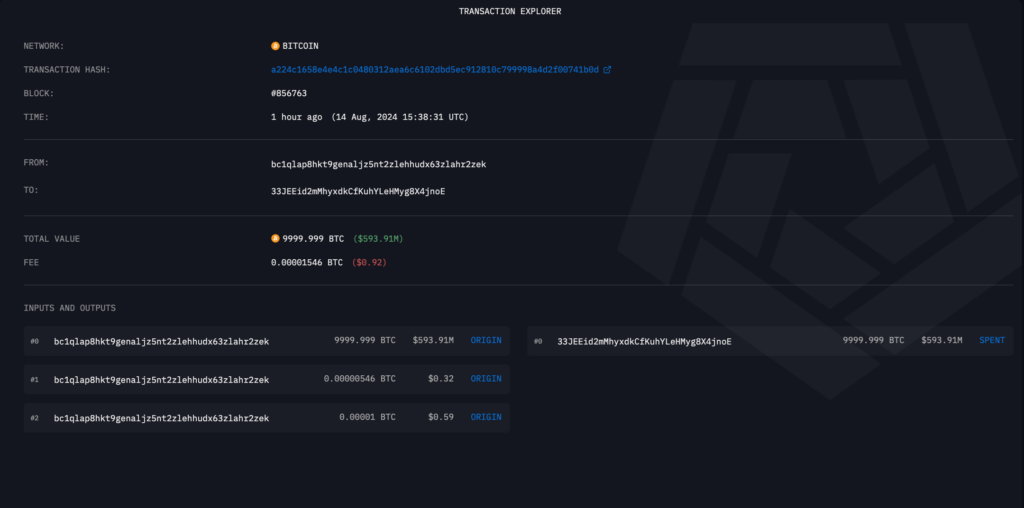
The US government transferred about 10,000 Bitcoins worth $58,525 on August 14, connecting them to an old Silk Road operation.
The US Department of Justice (DOJ) is actively changing laws and regulations about artificial intelligence in addition to cryptocurrency.
DOJ modifies AI policies to combat crime
The Department of Justice (DOJ) requested on August 7 that the US Sentencing Commission revise its guidelines to include harsher punishments for offences using artificial intelligence.
The suggestions aim to go far beyond accepted norms and cover crimes using AI and any crime assisted or encouraged by basic algorithms.



